AVIATORS MAGAZINE
News and features covering the entire aviation sector in Africa and beyond
Wednesday, 9 May 2018
NEW JKIA RUNWAY IN LIMBO
The construction of the Sh22 billion second runway at the Jomo Kenyatta International Airport is at hurdles following the government’s move to hold the process to review its economic value.
This comes just two years after the government cancelled plans for the constructing of a Sh56 billion Green Field terminal at the airport, saying there was no value for money in putting up the project, and opted for construction of the second runway instead.
The Ministry of Transport says that although the project has not been cancelled, the government is deliberating on its economic viability before it embarks on what it terms “capital intensive venture”.
“We have not cancelled the project. What we are doing right now is to deliberate on the full economic value of this project against other things,” said Transport and Infrastructure Principal Secretary Paul Maringa.
The Kenya Airports Authority (KAA) had already secured funding from African Development Bank (AFDB) for the runway. The bank approved Sh16 billion loan in November last year with the government topping up 20 per cent of the total cost.
“This is a heavy investment project and we have to be sure of its value before we embark on it, just to ensure that we get it right,” he added.
Prof Maringa said they want to understand the effectiveness of investing Sh21.9 billion on the runway against other projects, which he did not explain.
In February, KAA announced that the cost of the runway had been revised downwards from Sh37 billion to Sh21.9 billion.
If the proposed runway is cancelled, it will mark the second major project at JKIA to be financed by AFDB to have been abandoned by the ministry. The Green Field Terminal project was cancelled in 2016.
The Transport ministry said in March 2016 that the cancellation of the plan was informed by a finding that the terminal would yield little value for money and that the funds were better used at constructing a second runway.
“We have stopped the Greenfield project because it has no value for money. We would rather spend that cash building a second runway as opposed to a new facility,” said Transport Cabinet Secretary James Macharia in 2016.
The Greenfield terminal project was to meet the needs of the increasing number of passengers passing through Kenya’s main airport. It was to be built by a Chinese firm over a period of 36 months.
Sunday, 10 December 2017
KENYA AIRWAYS CEO SEBASTIAN MIKOSZ BLAMED ON SACKING KQ ENGINEERS
The Cotu boss says the move is unconstitutional and against workers' rights.
Wednesday, 8 November 2017
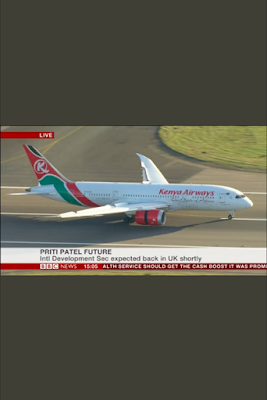
THOUSANDS OF BRITISH PEOPLE WATCHING ONE PLANE KQ100
Last night British cabinet minister Priti Patel was summoned back to London from a trip to Africa to meet prime minister after reports that she had secret meeting with Israeli officials. many expected her to be fired, but what caught our eye is the obsession the UK press had with her flight. According to flightradar254,KQ100 NBO 1HR 15;26 Was the most tracked plane on Wednesday.
HERE THE PHOTOS
Wednesday, 26 October 2016
Aviation Legend Bob Hoover Dies at 94
News of the death of legendary test pilot and aerobatics pioneer Bob Hoover this morning has brought grief to the aviation community.
Hoover, known among his many fans as the “pilot’s pilot,” died at about 2 a.m. PT, according to reports. He was 94 years old.
Hoover’s flying career began when he was a teenager. He soon enlisted and flew in World War II as a fighter pilot. After being shot down over Italy and spending 16 months in a German POW camp, he famously escaped by stealing a Fw190 fighter and flying it to the Netherlands.
He went on to become a U.S. Air Force test pilot alongside Chuck Yeager and later revolutionized aerobatics with his airshow routines in his instantly recognizable green and white Shrike Commander and yellow P-51 Mustang. The movie Flying the Feathered Edge: The Bob Hoover Project recounts his entire storied career in detail.
In addition to being one of the most accomplished pilots who ever lived, Hoover was also universally beloved by pilots and aviation enthusiasts. As news of his death broke this morning, the aviation world took to social media to mourn, share memories and wish one of the greatest aviators of all time blue skies.
Monday, 24 October 2016
KAA BOSS TO START WORK IN NOVEMBER
The newly appointed Kenya Airports Authority (KAA) managing director,Johnny Andersen is scheduled to start work next month,after he was appointed by Transport secretary James Macharia.
State House spokesman Manoah Esipisu said Sunday that Mr Andersen would take up the position in mid-November, dispelling any uncertainties about the July 16th appointment.
“Mr Andersen had asked for a six-month period to wind down his other engagements, but in the end an amicable agreement was reached. A timing that both the board and the ministry responsible are happy with,” Mr Esipisu said during a Press briefing at State House, Nairobi.Esipisu also said that the government had already issued the Norwegian with a work permit.
Anderson, a career aviation executive, joins the authority from Avinor AS, a state-owned firm that managed airports in Norway.
At Avinor, he the Director of national Aiports, responsible for seven state-owned airport buses.
His 21 years' experience includes managing airports in Norway, Denmark and Latvia.
"Andersen previously served at Vice President and senior Vice President for Ground Operations at AirBaltic in Latvia," Karangi said.
He said Andersen was also the director ground handling sales at Wideroes Flyveselskap AS in Norway.
Andersen holds a Masters of Science Degree in Air Transport Management from Cranfield University in UK and a Bachelor of Business Administration in Logistics from BI Norwegian School of Management in Norway.
"He has also studied Chinese Business, Trade and Commerce at Fundan University in China as well as Aviation Law at CAE Inc in the Netherlands," the KAA boss said.
Andersen is a fellow FRAeS at the Royal Aeronautical Society in the UK and an accredited instructor at IATA.
Sunday, 23 October 2016
A FLYING SCHOOL AIRCRAFT FORCED TO LAND AFTER A BIRDSTRIKE
A flying school light plane aircraft was today forced to return to wilson airport nairobi after a collision with an eagle.
Bird Strike is common and can be a significant threat to aircraft safety. For smaller aircraft, significant damage may be caused to the aircraft structure and all aircraft, especially jet-engined ones, are vulnerable to the loss of thrust which can follow the ingestion of birds into engine air intakes. This has resulted in a number of fatal accidents.
The nature of aircraft damage from bird strikes, which is significant enough to create a high risk to continued safe flight, differs according to the size of aircraft. Small, propeller-driven aircraft are most likely to experience the hazardous effects of strikes as structural damage, such as the penetration of flight deck windscreens or damage to control surfaces or the empennage. Larger jet-engined aircraft are most likely to experience the hazardous effects of strikes as the consequences of engine ingestion. Partial or complete loss of control may be the secondary result of either small aircraft structural impact or large aircraft jet engine ingestion. Loss of flight instrument function can be caused by impact effects on the Pitot Static System air intakes which can cause dependent instrument readings to become erroneous.
Complete Engine failure or serious power loss, even on only one engine, may be critical during the take-off phase for aircraft which are not certificated to 'Performance A' standards. In the case of bird ingestion into more than one engine, all aircraft are vulnerable to loss of control. Such hazardous ingestion is infrequent but may result from the penetration of a large flock of medium sized birds or an encounter with a smaller number of very large ones.
In some cases, especially with smaller fixed wing aircraft and helicopters, windscreen penetration may result in injury to pilots or other persons on board and has sometimes led to loss of control. (See the images at the foot of this article.)
Although relatively rare, a higher altitude bird strike to a pressurised aircraft can cause structural damage to the aircraft hull which, in turn, can lead to rapid depressurisation. A more likely cause of difficulty is impact damage to extended landing gear assemblies in flight, which can lead to sufficient malfunction of brakes or nose gear steering systems to cause directional control problems during a subsequent landing roll. A relatively common but avoidable significant consequence of a bird strike on the take off roll is a rejected take off decision which is either made after V1 or which is followed by a delayed or incomplete response and which leads to a runway excursion off the departure end of the runway.
A FLYING SCHOOL AIRCRAFT FORCED TO LAND AFTER A BIRDSTRIKE
A flying school light plane aircraft was today forced to return to wilson airport nairobi after a collision with an eagle.
Bird Strike is common and can be a significant threat to aircraft safety. For smaller aircraft, significant damage may be caused to the aircraft structure and all aircraft, especially jet-engined ones, are vulnerable to the loss of thrust which can follow the ingestion of birds into engine air intakes. This has resulted in a number of fatal accidents.
The nature of aircraft damage from bird strikes, which is significant enough to create a high risk to continued safe flight, differs according to the size of aircraft. Small, propeller-driven aircraft are most likely to experience the hazardous effects of strikes as structural damage, such as the penetration of flight deck windscreens or damage to control surfaces or the empennage. Larger jet-engined aircraft are most likely to experience the hazardous effects of strikes as the consequences of engine ingestion. Partial or complete loss of control may be the secondary result of either small aircraft structural impact or large aircraft jet engine ingestion. Loss of flight instrument function can be caused by impact effects on the Pitot Static System air intakes which can cause dependent instrument readings to become erroneous.
Complete Engine failure or serious power loss, even on only one engine, may be critical during the take-off phase for aircraft which are not certificated to 'Performance A' standards. In the case of bird ingestion into more than one engine, all aircraft are vulnerable to loss of control. Such hazardous ingestion is infrequent but may result from the penetration of a large flock of medium sized birds or an encounter with a smaller number of very large ones.
In some cases, especially with smaller fixed wing aircraft and helicopters, windscreen penetration may result in injury to pilots or other persons on board and has sometimes led to loss of control. (See the images at the foot of this article.)
Although relatively rare, a higher altitude bird strike to a pressurised aircraft can cause structural damage to the aircraft hull which, in turn, can lead to rapid depressurisation. A more likely cause of difficulty is impact damage to extended landing gear assemblies in flight, which can lead to sufficient malfunction of brakes or nose gear steering systems to cause directional control problems during a subsequent landing roll. A relatively common but avoidable significant consequence of a bird strike on the take off roll is a rejected take off decision which is either made after V1 or which is followed by a delayed or incomplete response and which leads to a runway excursion off the departure end of the runway.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)